Discover
our wide range
of topics
Trending topics from Health Care industry. Learn more about
Covid Pandemic etc.

February 28, 2025
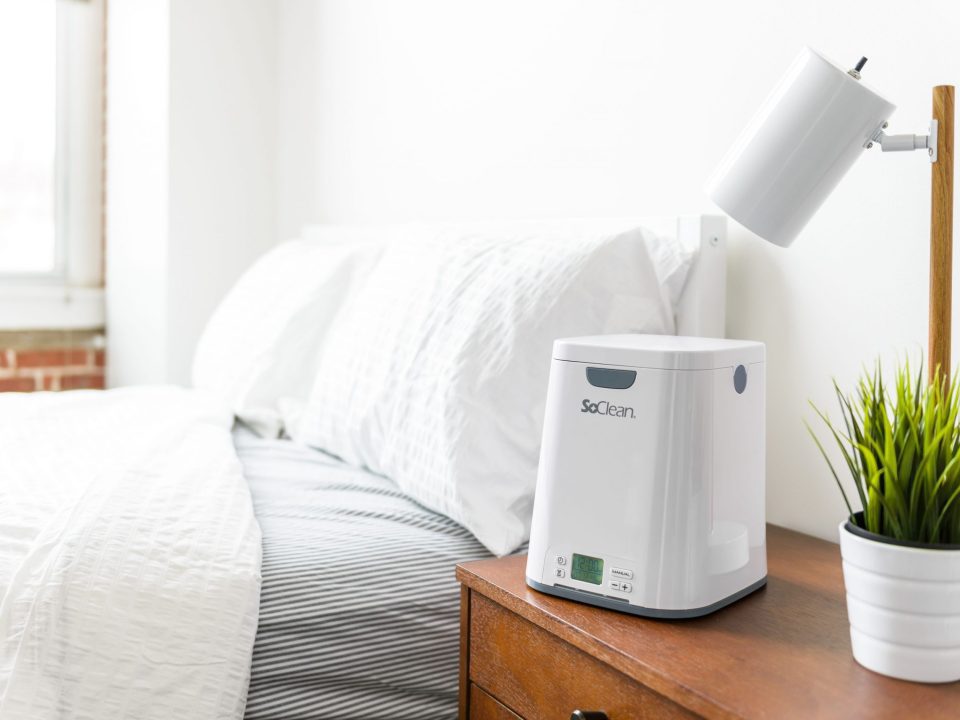
More and more people are using new technologies, like breathing machines, to help them get a good night’s sleep. CPAP machines, which stand for constant positive […]
February 21, 2025
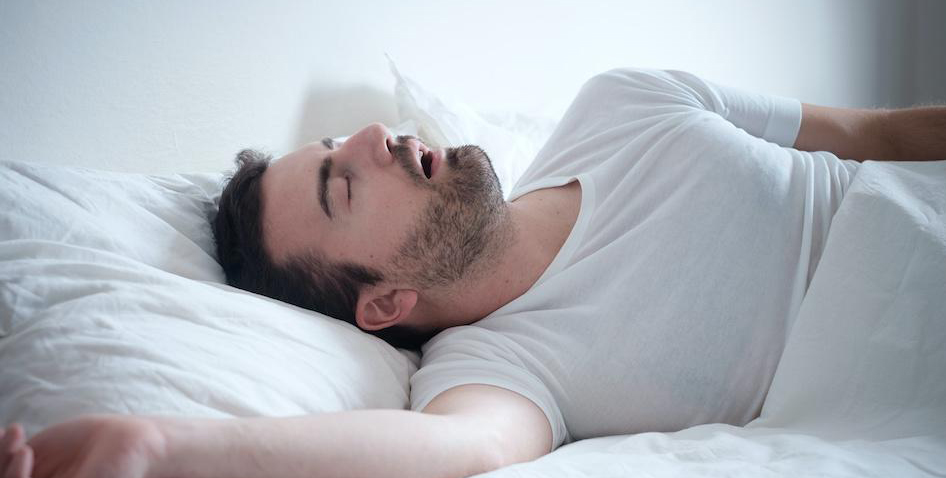
What is sleep apnea? Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder whereby a person stops repeatedly breathing while sleeping. It can cause health problems like high blood […]
February 13, 2025
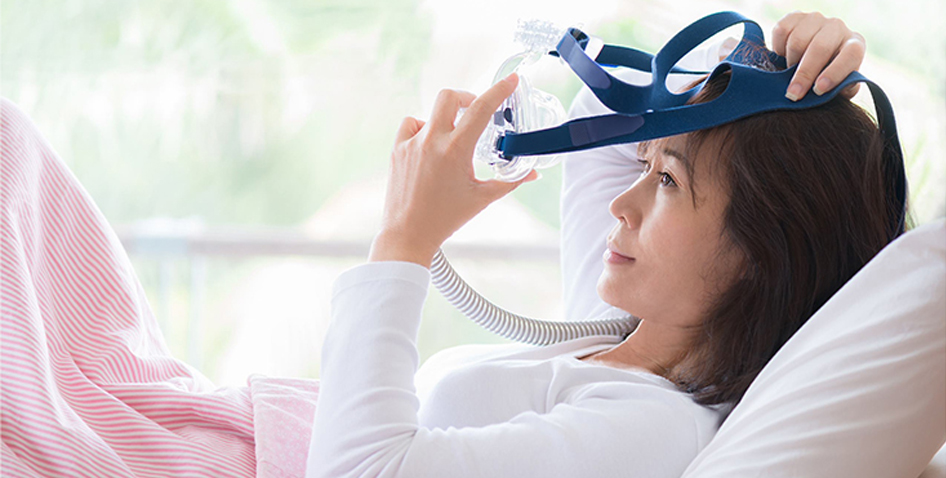
CPAP masks provide coverage of the face, including the nose and mouth. When selecting a CPAP mask, you need to check whether it is comfortable enough […]
February 6, 2025
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common but dangerous sleep disorder that affects millions of people all over the world. If you or someone you know […]
January 29, 2025
In the world of exercise technology, smart rings are the newest thing that everyone wants. Wearable tech is becoming more and more popular, and they are […]
January 22, 2025
Sleep apnea is a serious life-threatening sleep disease. In this breathing stops and begins repeatedly. You can have sleep apnea if you snore loudly and are […]